Urinary Tract Information

The urinary tract includes the bladder, urethra and kidneys (see figure). UTIs are common infections that happen when bacteria, often from the skin or rectum, enter the urethra and infect the urinary tract.
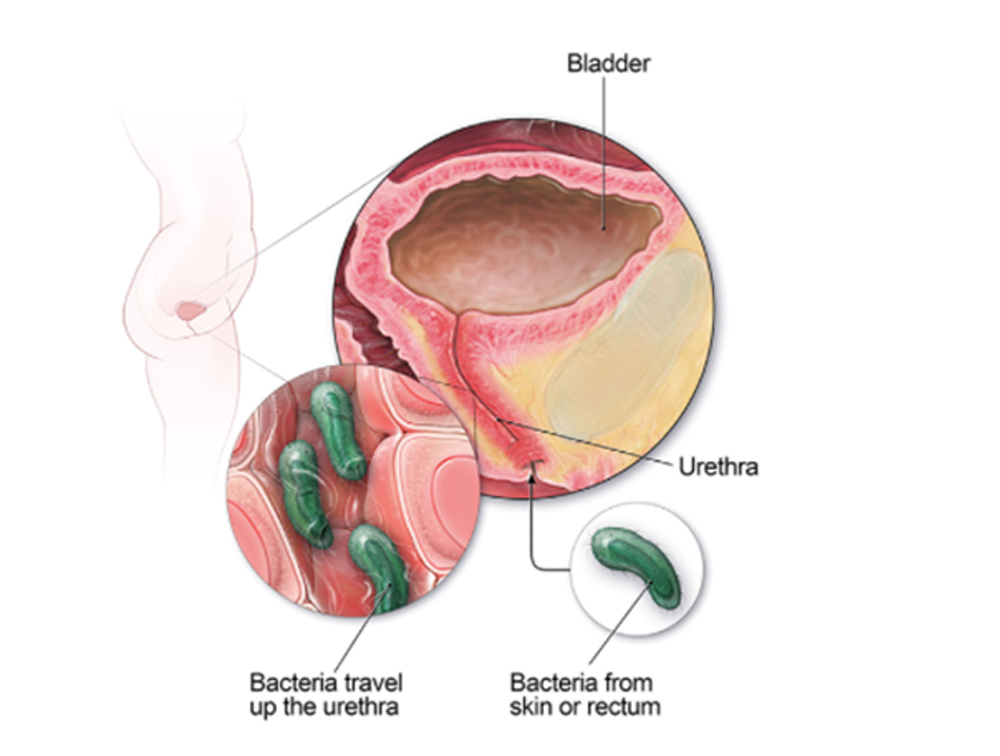
A female urinary tract, including the bladder and urethra. This image shows how bacteria from the skin or rectum can travel up the urethra and cause a bladder infection.
Types and strains
- Bladder infection (most common, also known as cystitis).
- Kidney infection (less common but more serious, also known as pyelonephritis).
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms of a bladder infection can include:
- Pain or burning while urinating
- Frequent urination
- Feeling the need to urinate despite having an empty bladder
- Bloody urine
- Pressure or cramping in the groin or lower abdomen
Symptoms of a kidney infection can include:
- Fever
- Chills
- Lower back pain or pain in the side of your back
- Nausea or vomiting
Younger children may not be able to tell you about UTI symptoms they are having. While fever is the most common sign of UTI in infants and toddlers, most children with fever do not have a UTI.
Risk factors
UTIs are more common in females because their urethras are shorter and closer to the rectum. This makes it easier for bacteria to enter the urinary tract.
Other risk factors:
- A previous UTI.
- Recent sexual activity.
- Changes in the bacteria that live inside the vagina or vaginal flora. For example, menopause or the use of spermicides can cause these bacterial changes.
- Pregnancy.
- Age (older adults and young children are more likely to get UTIs).
- Structural problems in the urinary tract, such as enlarged prostate.
- Poor hygiene, for example, in children who are potty-training.
Prevention
- Urinate after sexual activity.
- Stay well hydrated.
- Take showers instead of baths.
- Minimize douching, sprays or powders in the genital area.
- Teach girls when potty training to wipe front to back.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most UTIs can be cured. Bladder infection symptoms most often go away within 24 to 48 hours after treatment begins. If you have a kidney infection, it may take 1 week or longer for symptoms to go away.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Life-threatening blood infection (sepsis) — The risk is greater among the young, very old adults, and people whose bodies cannot fight infections (for example, due to HIV or cancer chemotherapy).
- Kidney damage or scarring.
- Kidney infection.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have symptoms of a UTI. Contact your provider right away if you have signs of a possible kidney infection, such as:
- Back or side pain
- Chills
- Fever
- Vomiting
Also contact your provider if UTI symptoms come back shortly after you have been treated with antibiotics
Prevention
Diet and lifestyle changes may help prevent some UTIs. After menopause, a woman may use estrogen cream around the vagina to reduce infections.
N.B. The content provided on this blog page has been sourced from definitive and credible resources to ensure accuracy and reliability. We do not claim ownership of all the information shared.
